Low-Resource Data Augmentation
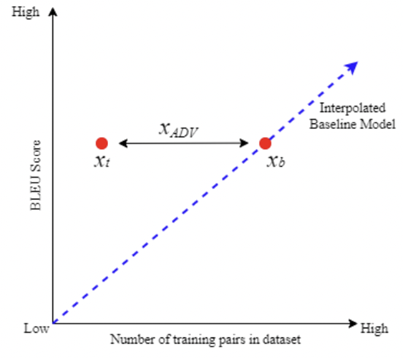
It’s common practice to measure the impact of data augmentation and neural architecture improvements for low-resource environments using artificial datasets—datasets created by simply taking a small amount of text from a high-resource language. Truly scarce global languages, such as Māori, Uyghur, and Kabyle, often has linguistic features that do not exist in high-resource languages, such as German, French, or English. Furthermore, the most common metric to measure machine translation performance, BLEU scores, are often difficult to interpret in low-resource environments. We need a new way to measure. In a recent paper [https://aclanthology.org/2023.loresmt-1.8/] , we introducing a new and simple way to measure the impact of data augmentation methods for extremely low-resource global languages.
Tech Stack
Neural Machine Translation, Data Augmentation, Python
Food Frame
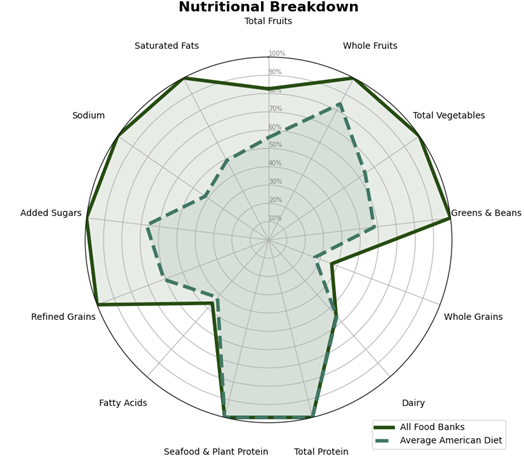
FoodFrame provides food bankers with new data-driven analyses of their nutritional and climate impact on target communities. Created in collaboration with non-project food banks, FoodFrame joins data from several national databases. Easily visualize the nutrition categories of a food supply or calculate the amount of food waste prevented by using or donating food sources from over thirty large food warehouses, nation-wide using a Stanford-made web app.
Tech Stack
Python, HTML, Streamlit, Data Analytics

Classical Atlas: A Python Package for Open-Access Geospatial Datasets
Classical Atlas is a Python package that makes it easier to work with data from Pleiades and other datasets linked by Pleiades IDs. Classical Atlas includes all the code required to parse the otherwise non-loadable main Pleiades JSON file. This package also mines connections from this dataset and builds a network structure representing geospatial relationships. By making this data available in an object-oriented format, more researchers are able to use this data in any manner they wish, even outside of network sciences.
Tech Stack
Python, HTML, JSON
Pyth-agora: Modeling Social Networks in Market Spaces
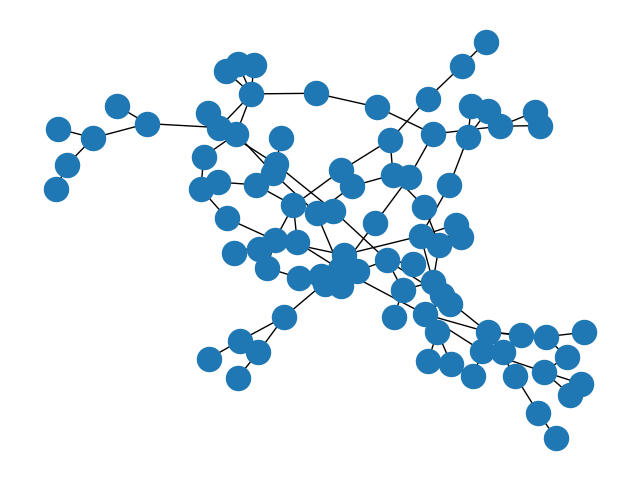
Pyth-agora is a code package for modeling the impact of select types of social networks on production and consumption outcomes. This multidimensional social landscape tests the impact of social relationships on individual consumption, and models how individual transactions accumulate to create long-term production and consumption trends.
Tech Stack
Python, Statistics, Data Simulation, Market Models